So you’ve heard about Bitcoin, but you’re not sure what it is? Before you rush into buying your first coins, it’s worth taking the time to learn the ins and outs the Bitcoin phenomenon. Otherwise, you run the risk of losing money – whether you sell bitcoins, fearing a drop in its price or due to bad custody decisions. This guide will help you understand what Bitcoin is, why it was developed and familiarize yourself with the basics of how it works.
This guide is based on the materials of now-closed “crypto” business. It has been revised and adapted by Tony. Support the project.
Learn why Bitcoin was created and why it is so valuable #
Bitcoin is designed to let you store, send, and receive money without any banks or credit card companies.
Until Bitcoin came around, you needed banks, credit cards, or companies like PayPal and Venmo to send and receive money. These companies were necessary to do something only they could do: verify that the person spending money actually has money to spend. Banks can do this because they hold everyone’s money, so they know all account balances.
But what’s so great about not using banks and credit card companies? For starters, they are slow, expensive, and part of a broken financial system.

Banks have huge costs for buildings, lawyers, and highly paid executives - all funded by the fees you pay (and massive taxpayer bailouts, like in 2008). Banks also limit how you can access and send your money.
In 2008, a mysterious person calling himself Satoshi Nakamoto invented Bitcoin. To this day, Satoshi remains anonymous and nobody knows who he or she is.
Satoshi could be a woman, a man, or a group of people. Nobody knows! What we do know is that the bitcoin.org domain was registered in August 2008. Then, in November, Satoshi posted the famous Bitcoin Whitepaper.
The first Bitcoins were issued in January 2009. Embedded in the first Bitcoin code was the message “Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks.” - hinting at Bitcoin’s creation because of the 2008 financial crisis.
Bitcoin’s breakthrough is that it’s the first to solve a problem so tough, it has its own name: The Double Spend Problem.
Here is how the Double Spend Problem works: Digital money is just like a computer file, so it would be easy for somebody to just “counterfeit” it by copy and pasting. Before Bitcoin, the solution was for banks to keep track of the money in everybody’s accounts, so that nobody could spend money twice.
Bitcoin solves the Double Spend Problem differently. It makes all accounts and transactions public - but without revealing private details like your name. Since account balances are public, it would be obvious if someone used the same money twice.
Once bitcoin is sent, it’s publicly added to the receiver’s account. So if a scammer tries to spend their Bitcoin twice, it’s easily discovered and prevented.
Solving the Double Spend Problem is a big deal. It allows bitcoin to be sent directly from one person to another, without using ANY third party like a bank.
Not needing a third party (like a bank) to handle accounts and transactions has a lot of benefits. Transactions can be faster and cheaper since there is no middleman.
Plus, your personal information becomes more private since no bank has to store it. You’re probably beginning to see why Bitcoin is such a game changer.
Let’s talk about why Bitcoin is so unique and revolutionary #
Bitcoin is a new form of money that’s completely digital. It can be used by anyone, anywhere in the world. There are no dollars, euros, pesos, or yen - it’s a universal currency.
Unlike traditional forms of money, there are no physical bitcoins. No dollar bills, no metal coins, no plastic cards – it’s 100% digital! Everything is done from phones and computers. This allows for fast and cheap transactions around the world and around the clock.
Incredibly, Bitcoin is not controlled by any person, company, or government. It’s run by the community of its users. Read that twice, because it’s important!
Bitcoin users are located all around the world and use the internet to help send and receive payments. But unlike traditional payments that pass through banks, bitcoin is sent directly from person to person, instead of from person to company to person. This is known as a peer-to-peer system (P2P). It means there is no central control.
What’s amazing is that none of the users in the Bitcoin community need to know each other for this system to work. You can send and receive bitcoin online without needing to meet or even trust the other person. We’ll explain how that’s possible in a bit.
Bitcoin has benefits that make it better than traditional money, banks, and credit card companies. Let’s explore what makes Bitcoin so unique.
Bitcoin was designed to solve problems that existed with the traditional banking system. But by finding a clever solution to the Double Spend Problem, Satoshi also created a better type of money. In fact, he was able to completely reinvent how money works.
Benefit 1 - Decentralization
Traditional money is controlled by banks and governments – which makes it a “centralized” currency.
Traditional money is controlled by banks and governments – which makes it a “centralized” currency.
Bitcoin is not controlled or regulated by any single entity like a bank – which makes it a “decentralized” currency.
Having no banks in control makes sending and receiving money cheaper, faster, and easier.
Not having banks involved means nobody can deny your application, nobody can close your account, and nobody can charge you outrageous fees. In short, banks are no longer in charge. This is what makes decentralized money so powerful.
Over 2 billion people worldwide can’t even get access to bank accounts! This prevents them from connecting with the rest of the world – they’re excluded. To them, a bank is like a fancy club they can’t get into.
Bitcoin will give them the benefits of a bank, without needing a bank. Anyone with a smartphone and internet connection is welcome!
Benefit 2 - No Counterfeit Money
Paper currencies, credit cards, and checks can be counterfeit. If you’ve ever been a victim of fraud, you know how much this sucks.
Bitcoin solves the Double Spend Problem which means criminals cannot create fake bitcoins. Counterfeiting is impossible.
Counterfeit traditional money is very common. In the U.S. alone it is estimated that between $70 and $200 million in counterfeit bills are in circulation. That’s up to 1 out of every 4,000 real bills. For Bitcoin, this issue simply doesn’t exist. Plus, you won’t have to pay those high fees for fraud protection!
Benefit 3 - Limited Supply
Traditional money is created by governments in unlimited quantities. They print more constantly, which decreases the value over time.
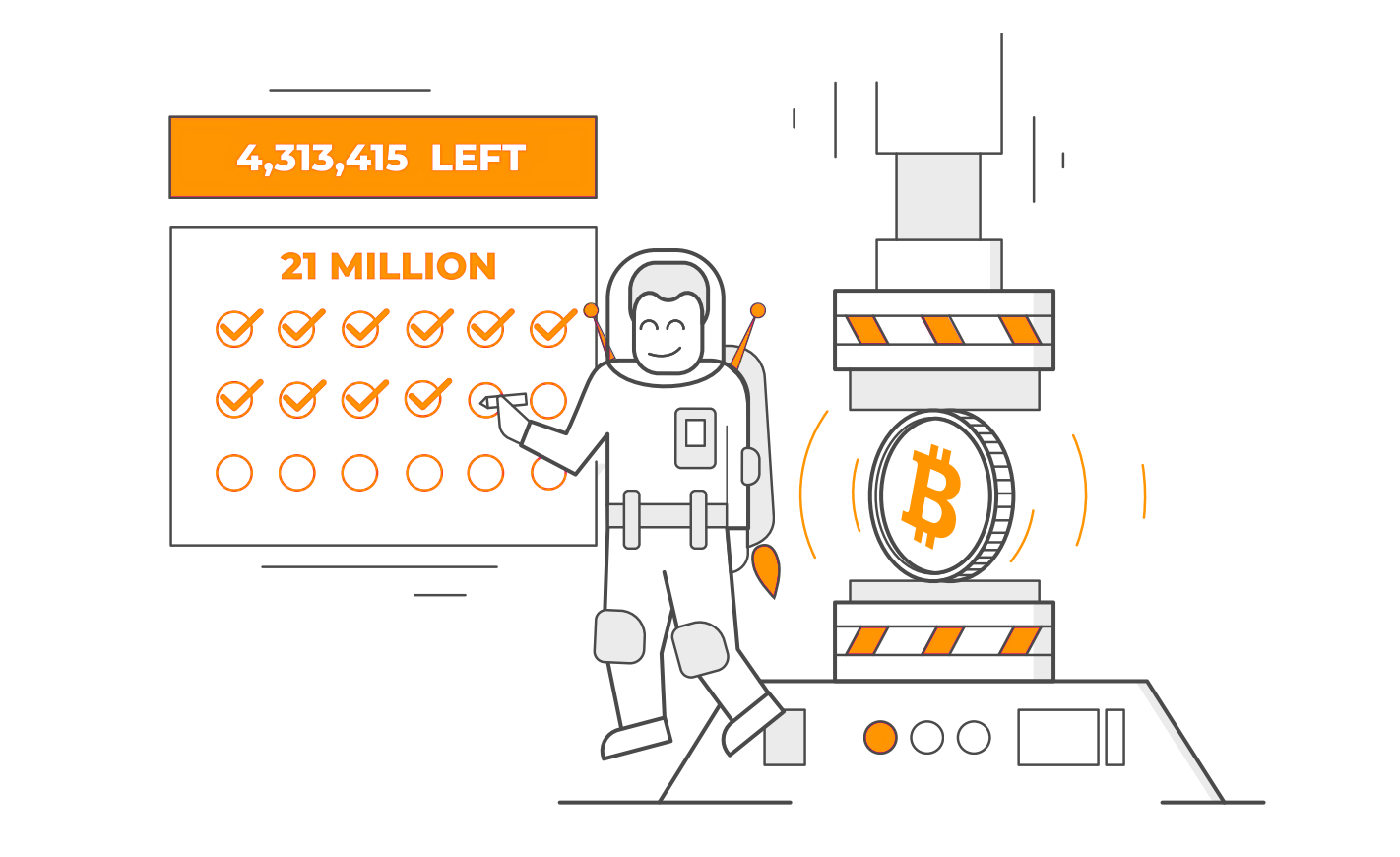
Bitcoin’s supply is limited to 21 million coins. There can never be more! Why? It’s designed to be scarce so that it increases in value over time.
A constantly increasing supply of money creates something called inflation. This means that the money you are holding is worth a little less every day. If you’re working hard and trying to save up, that’s bad. It’s why an ice cream was $0.05 in 1950, but is $5.00 today… traditional money keeps losing value.
Bitcoin’s limited supply creates the opposite effect, called deflation. This means the value of each Bitcoin is designed to increase over time. It’s part of the reason why so many people are excited about investing in Bitcoin.
Benefit 4 - Divisibility
Old fashioned money can be spent only in amounts as small as a single cent (so up to 2 decimal places).
Bitcoin can be spent in much smaller amounts, called Satoshis (all the way up to 8 decimal places). This means that it can be used even for tiny purchases.
Bitcoin is highly divisible because its value is designed to increase over time (through deflation). This divisibility means you can spend very small amounts of a bitcoin. So basically, an ice cream cone may cost 0.001 bitcoin today, but in the future it may cost 0.00000010 bitcoins, if bitcoin’s value rises even more.
A practical example where Bitcoin’s high divisibility is useful today is for microtransactions. These are very small payments used for digital goods and services. For example, imagine paying only a tiny amount of bitcoin for every page of an ebook you read, instead of paying for the whole book.
Microtransactions are something traditional money can’t do, because cents are not divisible enough and therefore too big for very small purchases.
Benefit 5 - Security
There is a lot of money stored in Bitcoin, so it needs to be very secure. Bitcoin uses cryptography to securely send payments.
That’s why Bitcoin is called a cryptocurrency. The code is so strong that tampering is virtually impossible. There is A LOT of money held in Bitcoin, but it has never been hacked!
In simple terms, cryptography is a technology that protects information through complex math functions. Bitcoin uses strong cryptography to protect your account and let you securely send money. It’s designed so that nobody can hack your account, and it prevents the wrong person from receiving your money.
Let’s now see how Bitcoin actually works #
Imagine four strangers sitting in a room, each with their own notebook. Because they are strangers, they don’t know or trust each other.
The four strangers in this example represent Bitcoin’s community of users. We are using strangers to explain this, because in the real world, most Bitcoin users do not know each other. The notebooks in this example represent what’s called the Bitcoin Blockchain. The Blockchain stores a public record of every single bitcoin transaction ever made. The Blockchain is not on paper but 100% digital and public.
Most importantly, there are thousands and thousands of identical copies of the Blockchain held by users around the world. All these copies are kept in sync by the system that runs the Blockchain.
One stranger gives one bitcoin to another stranger. Now, EACH of the four strangers records this transaction.
They then compare all their notebooks to make sure they match.
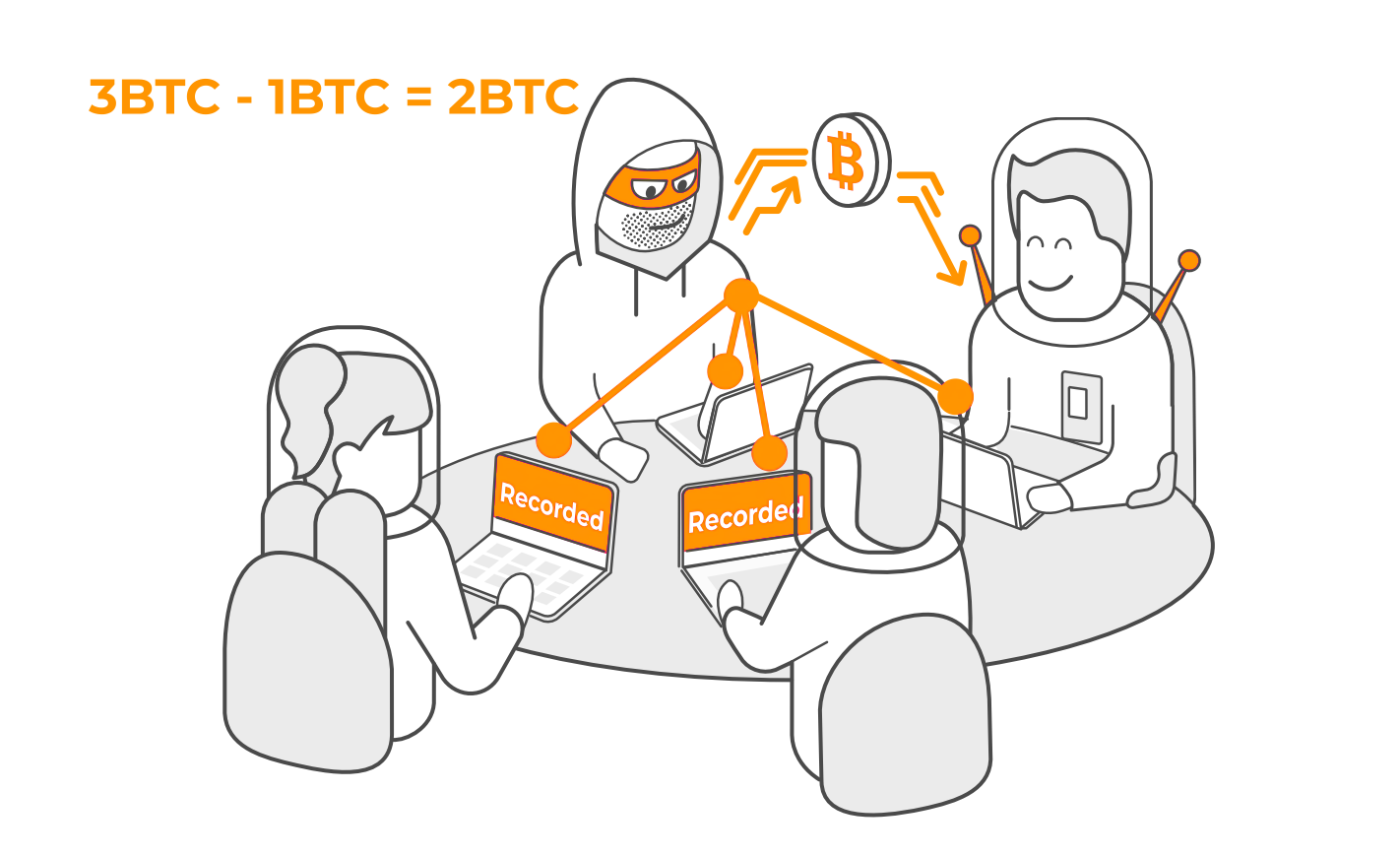
Just like in the example, when bitcoin is sent, the transaction is recorded on EVERY one of the thousands of copies of the Bitcoin Blockchain around the world. Each copy is an identical record of all transactions.
Just like notebooks were compared in the example, the Bitcoin system is constantly comparing all copies of the Blockchain to make sure they all have matching transactions.
If all four notebooks match up, everything is fine. The transaction is approved by everybody.
If one notebook is different from the other three, we have a problem. It means one stranger is lying about the transaction. We also know which stranger is lying (hint: it’s the one with the notebook that doesn’t match the others). As a result, the three others ignore the notebook that doesn’t match and move on. The transaction is not approved.
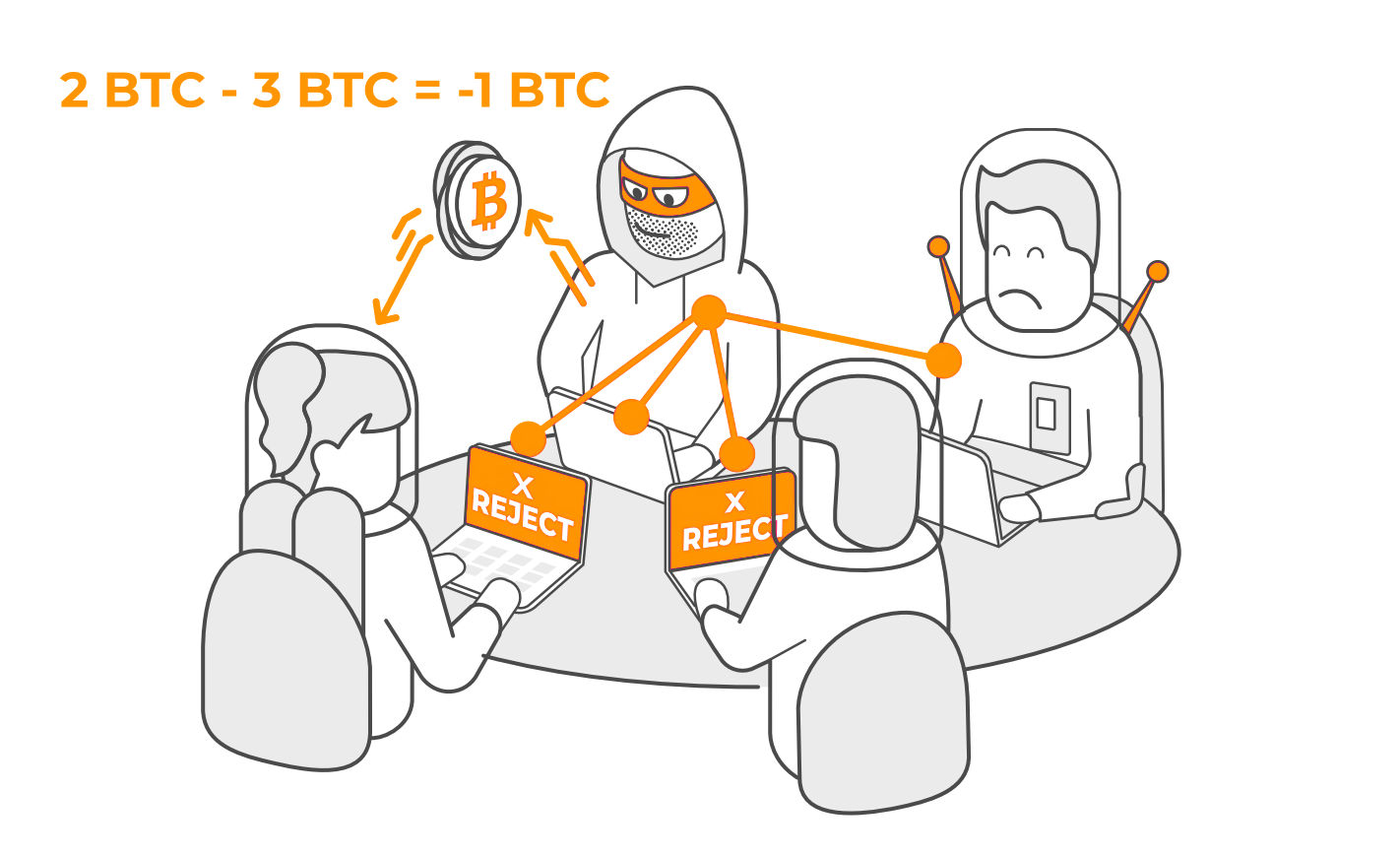
The same two outcomes can happen with Bitcoin: If all Blockchain copies match, everything is fine and the transaction will proceed.
If one Blockchain copy is different from all others in the Bitcoin network, the network automatically rejects the transaction that doesn’t match the rest. This is what prevents fraud. It’s impossible for scammers to manipulate the system, since their Blockchain copy wouldn’t match what everyone else agrees on.
Bitcoin works exactly like the notebook example. Each Bitcoin user has an identical copy of the Bitcoin “notebook” which publicly records all transactions. All notebooks get constantly compared to make sure they match.
Additionally, Bitcoin stores all past transactions permanently so that there is a record of where all bitcoin currently are. This proves who owns which bitcoin.
In short, the Bitcoin Blockchain knows where every single bitcoin is at all times. This is very powerful since it proves ownership without needing a third party like a bank.
Traditional currencies don’t have a Blockchain, so in some cases you can’t prove who owns what. This makes fraud and theft easier. For example, imagine somebody steals $20 in cash from you. You can’t easily prove who owns it.
The technology that stores and constantly compares Bitcoin’s “notebooks” to make sure they are all identical is called the Blockchain.
Bitcoin’s Blockchain is the technology that allows strangers to work together to exchange money without trust. This means no middlemen like banks are needed.
Instead of recording transactions in private record systems like a bank or credit card company does, Bitcoin users record ALL transactions at the SAME TIME in IDENTICAL copies of the Blockchain. As a result, any attempt to fool the system would be noticed as obviously different and rejected by the system.
This method of comparing all the identical “notebooks” is called finding a “consensus” - in other words a mutual agreement that the transaction isn’t fraud.
Bitcoin uses the same strategy to compare all transactions on the Blockchain. It can do this very quickly by using powerful computer code. The process of comparing transactions using this computer code is known as Bitcoin’s Consensus Algorithm.
Blockchain is the technology that makes Bitcoin so valuable, because it removes the need for a costly third party (like banks and credit card companies) to check transactions.
With Blockchain, total strangers can now exchange money without any trust and without any third parties being required. That’s revolutionary!
Remember the tricky Double Spend Problem from before? The Blockchain is what Bitcoin uses to prevent this problem from ever happening.
Once a bitcoin changes hands the transaction becomes an official Blockchain entry that’s automatically and permanently recorded, so the money can’t be spent twice. (Huge) Problem solved!
Now that you know how Bitcoin and the Blockchain work, let’s look at transactions #
Just like real money, bitcoin is stored in wallets. But Bitcoin’s wallets are (surprise, surprise) digital.
It seems weird, but your wallet doesn’t actually “hold” your bitcoins on your computer or phone. Instead, your wallet simply grants access to your bitcoins, which are recorded on the Blockchain itself.
Your Bitcoin wallet is like a bank account. It’s how you access your money.
Each Bitcoin wallet has a unique address so you can send money to and from it.
You can picture the Bitcoin wallet address like a bank account number. It’s used for the same purpose: To make sure bitcoin is sent to the right wallet (account).
A Bitcoin address is just a string of numbers and letters. It’s the only piece of information required to send and receive Bitcoin, so your name is not shared.
To send bitcoin from one wallet to another, you first need to authorize the transaction.
Just like in real life, you authorize transactions through a signature. For Bitcoin, this signature is done with a password called your private key.
Your Bitcoin private key works like a password, but it’s really your digital signature. It proves that it was you who authorized the transfer. It’s very important that you always keep your private key secret- it’s called private for a reason.
Bitcoin’s system actually uses two types of keys: Public and private. The best part? You don’t actually have to deal with any of these details. It’s all done automatically by your wallet. All you use to receive money is your Bitcoin address.
Let’s use an example to put it all together: Say Bob wants to send Jane one bitcoin.
The bitcoin will be sent from Bob’s wallet to Jane’s wallet. To do this, Bob enters Jane’s Bitcoin address, and then his wallet uses the digital signature (private key) to authorize the transaction. Boom, now the bitcoin is on the way!
Unlike depositing a check or cash, Jane doesn’t have to do anything to receive the money. More importantly, no third party (like a bank) has to process the transaction or can stop it.
Once Bob hits “Send” his bitcoin transaction is added to the Blockchain for processing.
Bob’s bitcoin transaction isn’t actually sent quite yet. Instead, Bob only announced that he wants to send his bitcoin. Next, the community of users verifies that Bob actually has enough bitcoin to send. Remember, this verification is done automatically by comparing Blockchain copies. Once verified, Bob’s bitcoin is on the way. Woosh!
Here is how processing works: Transactions from the last 10 minutes are bundled together. Each of these bundles is called a block. Together, the blocks form the Blockchain, hence the name.
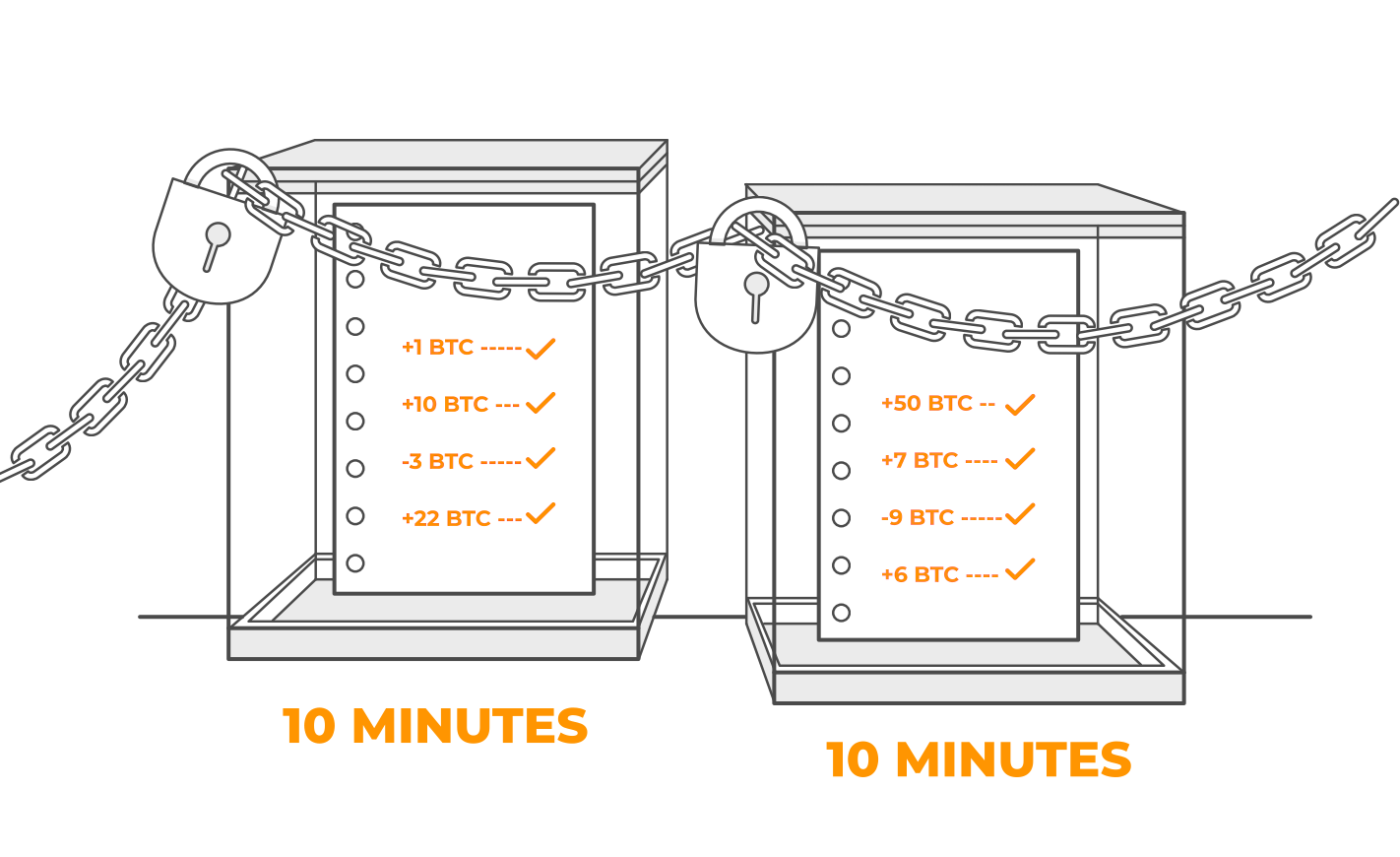
All Bitcoin transactions are bundled and added to blocks in order. Each Bitcoin block gets filled up with new transactions until it’s full. Overflowing transactions are simply added to the next block.
So who bundles and processes bitcoin transactions? That’s done by users called miners. Miners bundle transactions, verify them, and add them to the Blockchain.
Here is the interesting part: Miners do this work because they get paid in bitcoin for every block they add and for every transaction they process. In fact, they get brand new bitcoins which were just created by the system. That’s how bitcoin are born!
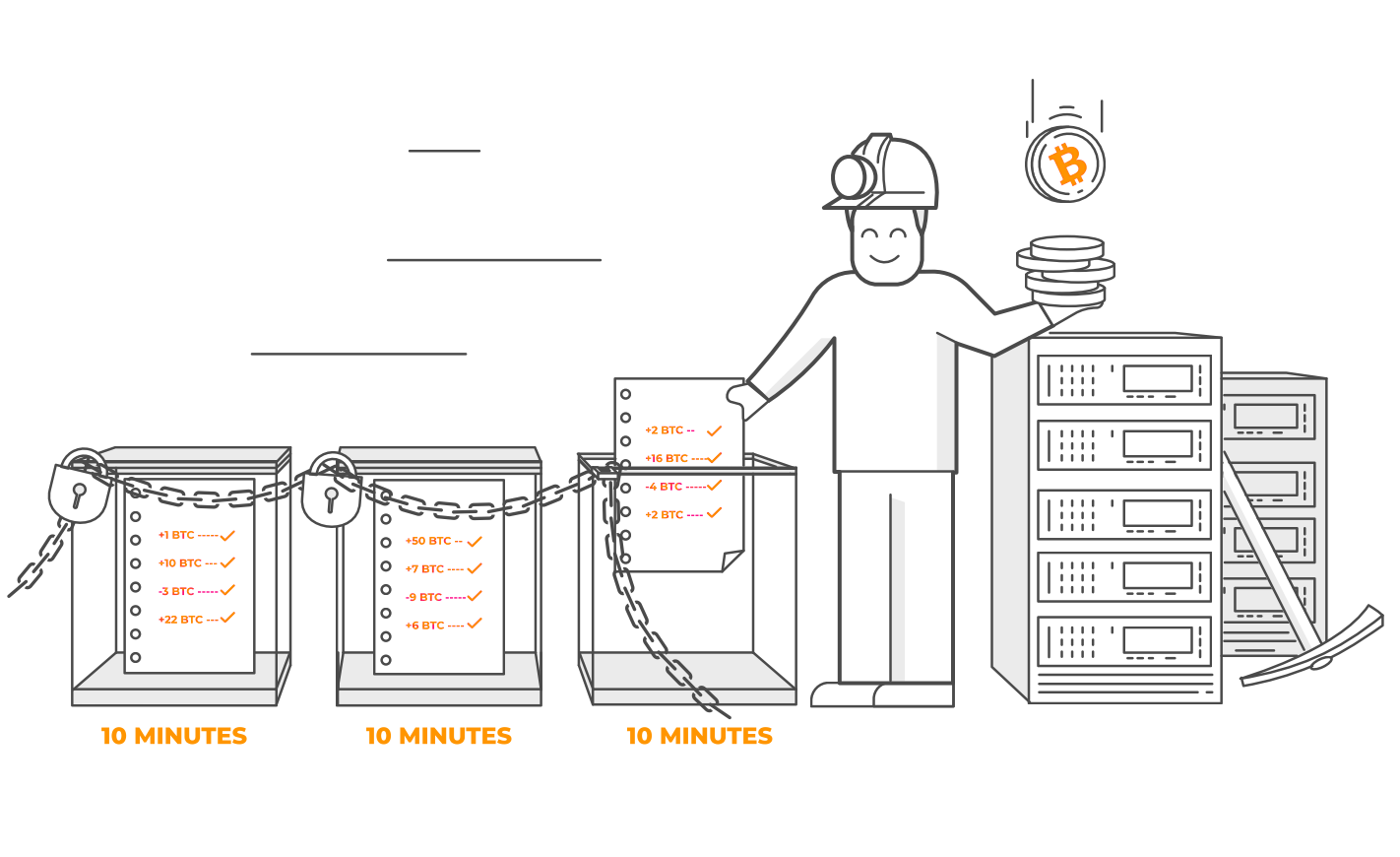
There are a lot of miners and they are all competing to add the next block to the Bitcoin Blockchain to get paid. There is a fixed total number of bitcoin. Every 10 minutes, new bitcoin are released and miners compete to earn them.
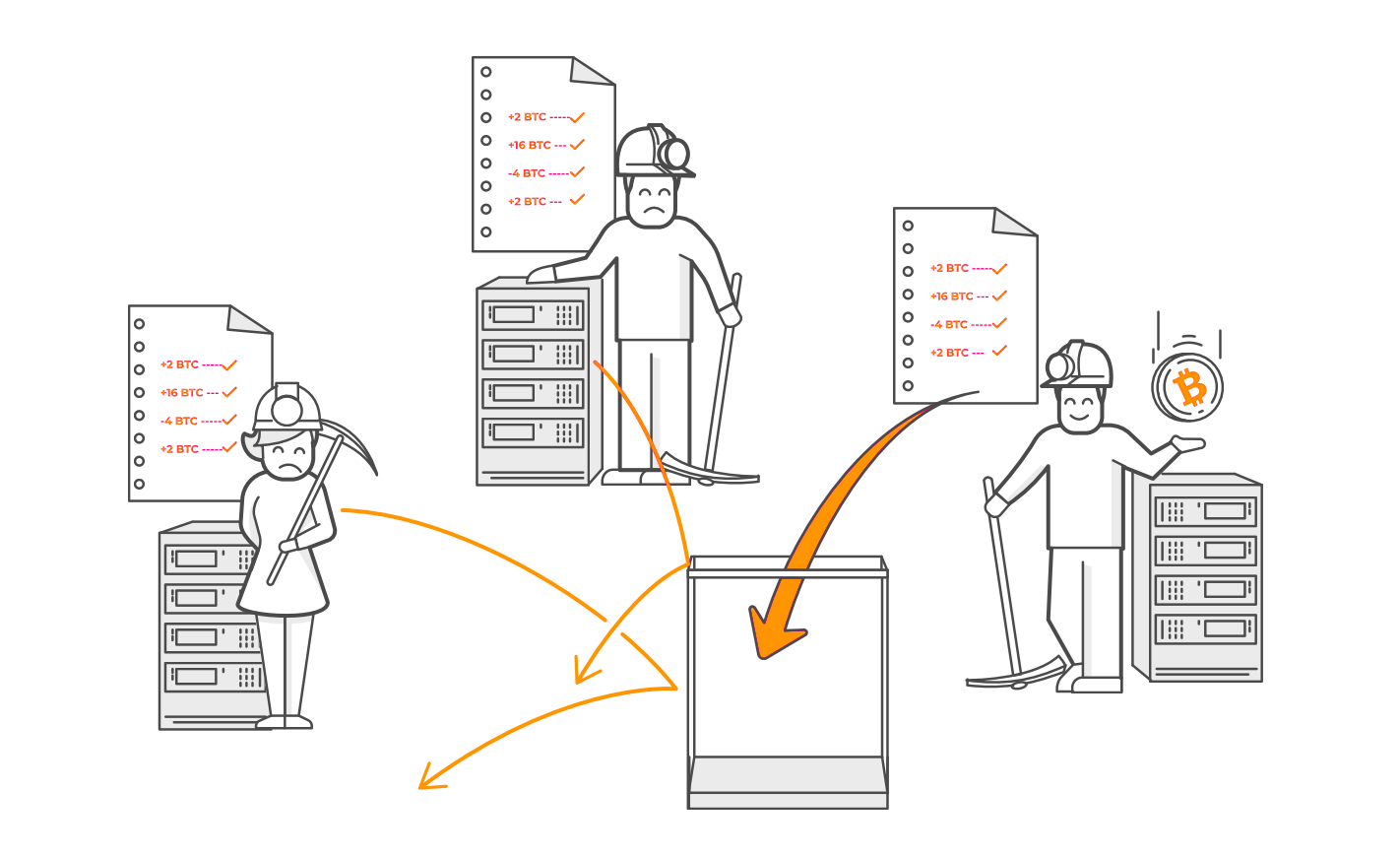
This process will continue until the year 2140 when all 21 million bitcoins have been created. There can never be more! After that, miners will continue to get small transaction fees, but no new bitcoin.
You now know what makes Bitcoin so unique. It is a clever system that allows complete strangers to securely send money directly between each other – no trust required! Amazingly, no third party (like a bank) is required, either.
Bitcoin is revolutionary because it gives you full control over your money, from ownership all the way to transactions. It’s this power that makes it so successful.
Every day, a lot of new people are trying out Bitcoin. They have realized that a brand new type of money has arrived. Bitcoin’s goal is to change the world and put you in the driver’s seat. Bitcoin is fast, reliable, cheap, simple, and secure. And it’s just getting started!
Have you enjoyed our guide to the basics of Bitcoin? Skip ahead to practical part of Intro to Bitcoin, where we cover the basics of interacting with Bitcoin - everything from buying to the possibilities of spending bitcoin, how to store it, and the basics of how to ensure the security and privacy of interacting with Bitcoin.👇